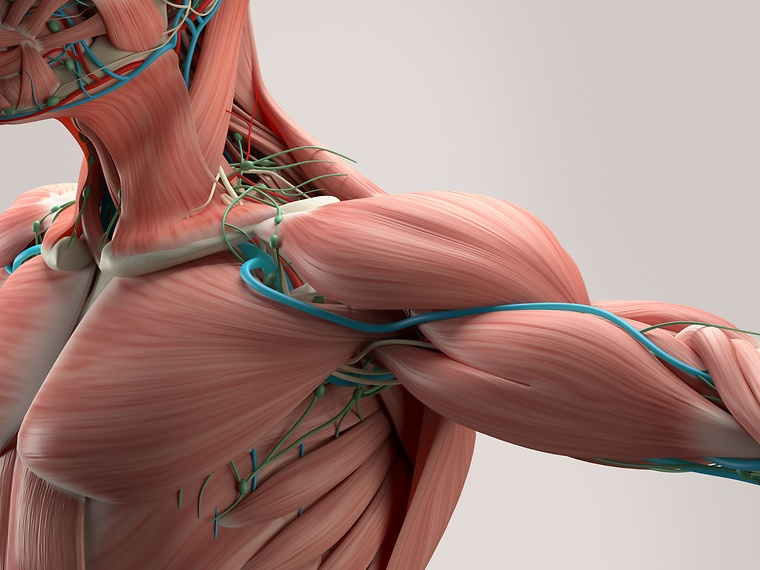
Overarching function
The muscle system is an organ system that has three main structures: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. The three structures work together to support the body’s movement, provide protection, and regulate temperature.
Basic structures and functions
Macroscopic structures
The three main muscular structures are smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscles. Of the three, only skeletal muscles are voluntary, meaning that you can consciously control them. Skeletal muscles are found to be attached to bones through tendons. The main purpose of skeletal muscles is to move the skeleton and shiver to conserve heat. Cardiac muscles are found in the heart, and is used for pumping blood through the body. Smooth muscles are found in the digestive system and blood vessels. They help the body move semi-fluids like food, water, blood, urine, and feces. Cardiac and smooth muscles work together to provide blood flow to the body.
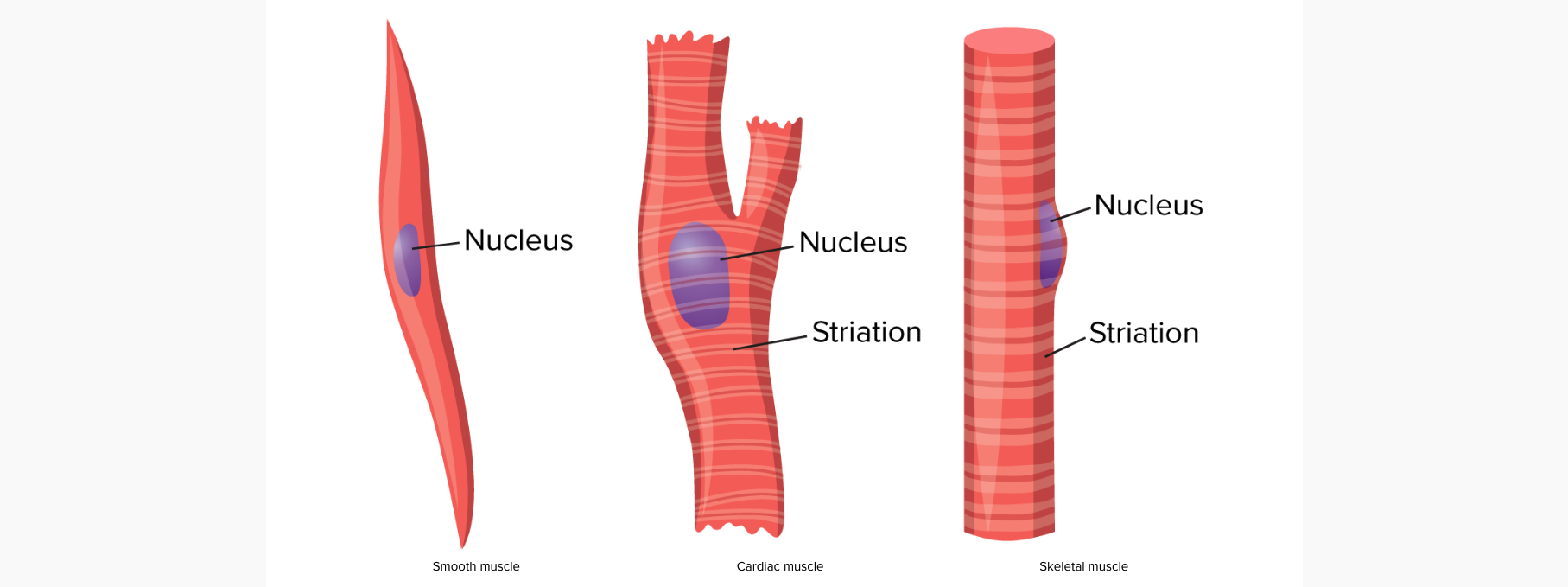
Microscopic structures
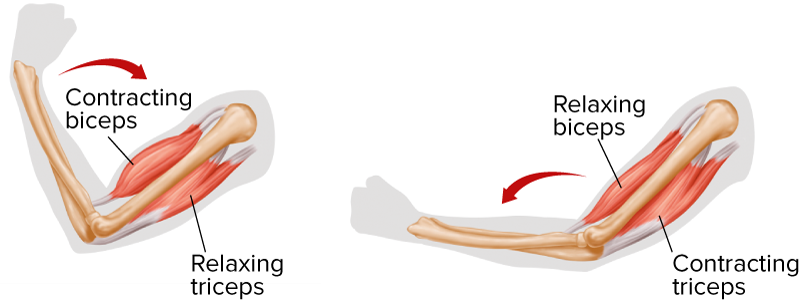
Most skeletal muscles are arranged in opposing, or antagonistic pairs. This means that typically, when one muscle contracts, the other relaxes, as shown in the diagram below. Skeletal muscle is arranged into fibers, which are essentially muscle cells. Fibers are made up of smaller units called myofibrils, which includes even smaller units called myosin and actin. The two smallest units are protein filaments, which are protein that gives the cell its rigidness. Myofibrils are then arranged in larger sections called sarcomeres. Sarcomeres are the functional units of the muscle and can be contracted or relaxed.
Connection to other systems
Smooth muscles connect to tendons on the skeleton to move the body. The cardiovascular system is also involved with the muscular system. Cardiac muscles are involuntary, and help pump blood from the heart to the farthest ends of the body. Smooth muscles are also involuntary, and connects with the digestive system. Smooth muscles help move semi-fluids such as food, water, urine, and feces. Smooth muscles are also found in blood vessels. In addition, when the nervous system detects low body temperature, the muscles can shiver to generate heat.
Differences between a frog and human
The frog’s muscular system is mainly specialized in jumping, whereas the human muscular system has to complete complex actions, such as standing, running, or sitting. In addition, frogs can stand with four legs, whereas humans have to stand upright with 2 legs. Our muscular system is more powerful and extensive in order to balance ourselves. The other main difference is that frogs do not have a diaphragm, which helps us to breath involuntarily.