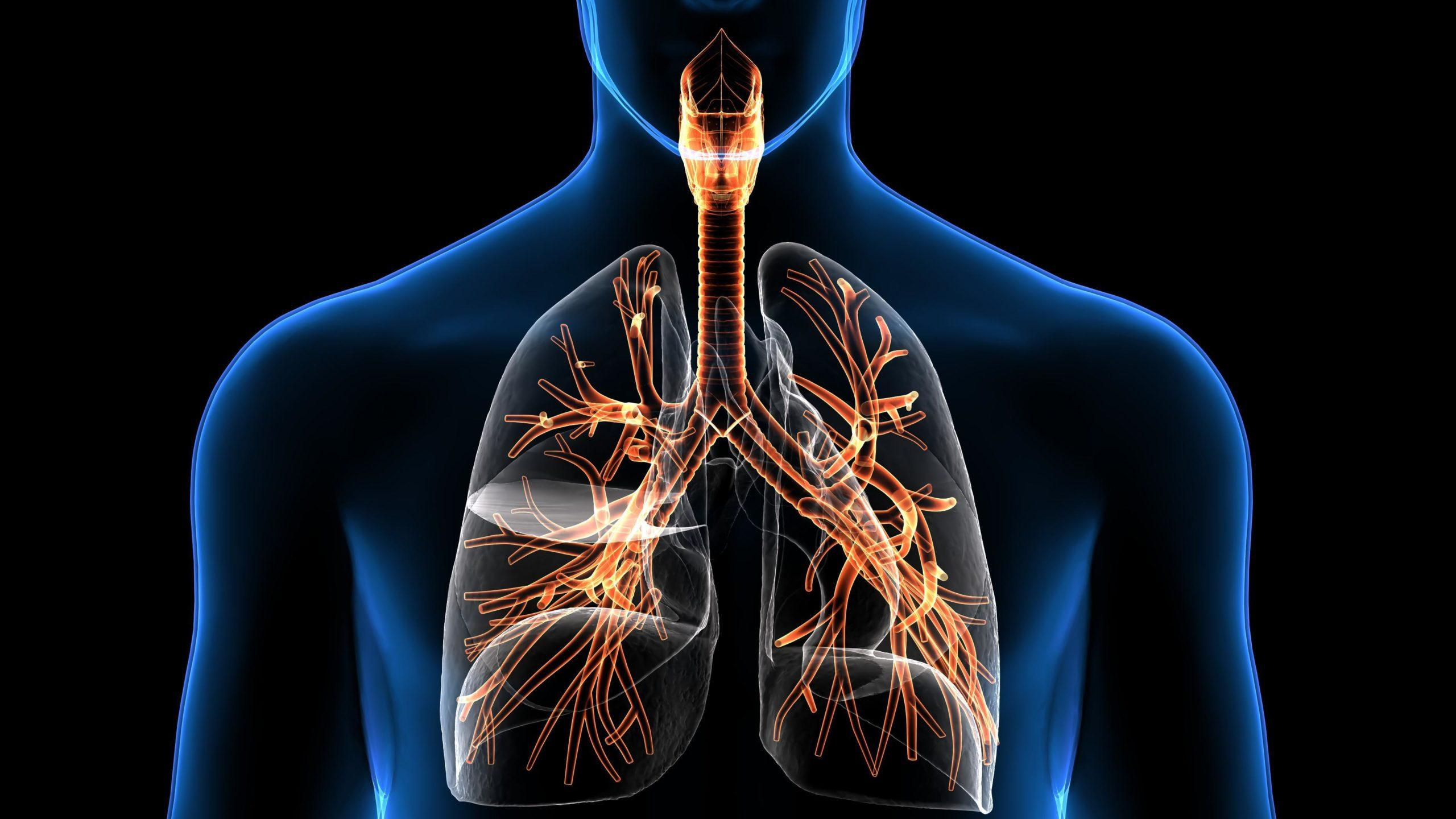
Overarching Function
The respiratory system has two main functions: breathing and respiration. Breathing is an involuntary action of the mechanical movement of air. Respiration is about exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide in the bloodstream.
Basic structures and functions
Macroscopic structures
-
Lungs
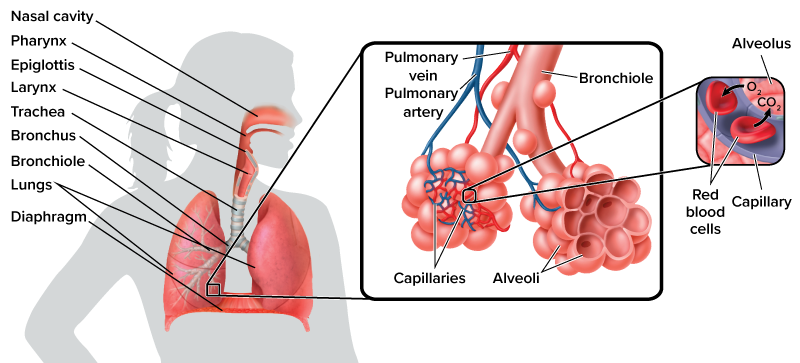
The lungs are the largest organs in the respiratory system. External respiration occurs at the lungs. The trachea moves inhaled air to the lungs through bronchi. In the lungs, inhaled oxygen moves into capillaries and is transported to body cells, whereas carbon dioxide will be exhaled from the lungs.
-
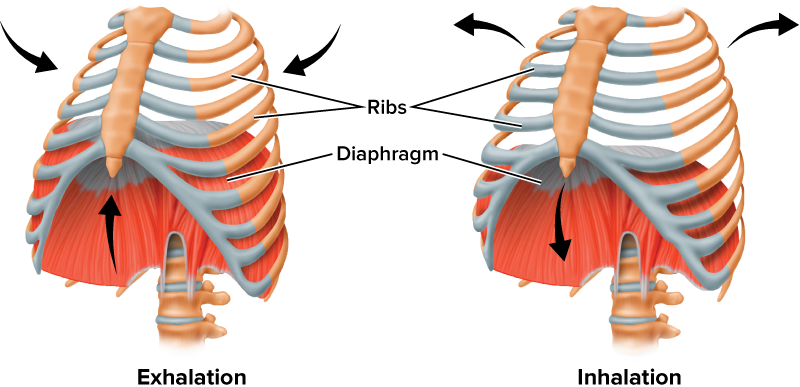
Diaphragm
The diaphragm enables the movement of air. When you inhale, the diaphragm contracts and allows air to move into the lungs. When you exhale, the diaphragm relaxes, reducing the size of the lungs and moves the air out.
Microscopic structures
-
Alveoli → Gas Exchange
Alveoli are the tiny air sacs at the ends of bronchioles. Gas exchange occurs at the alveoli. The oxygen inhaled from the air passes through the alveoli, from the capillaries the into the red blood cells. Then, it travels to other tissue cells in the body through the process of internal respiration. Carbon dioxide in the blood diffuses into the alveoli and gets exhaled during external respiration.
-
Bronchioles
Bronchioles are airways branched off from bronchi. The bronchioles carry air to the alveoli, since they are linked to each other.
Connection to other systems
The respiratory system connects with the circulatory system, providing the blood with ample oxygen and removing the unnecessary carbon dioxide. The respiratory system is responsible for bringing oxygen into the body and moving carbon dioxide out of the body, whereas the circulatory system is responsible for moving oxygen from the lungs to other cells via blood vessels and removes carbon dioxide out of the body through lungs.
Differences between a frog and human
Human has a more densely packed alveoli than a frog because we breathe only through our lungs. Human uses our mouth and nose to breathe whereas frogs breathe through their noses. In addition, the most obvious difference is that frogs can use their skin to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide. Their moist skin allows the process to function properly.