Overarching function
The skeletal system makes up the framework of our body. It enables us to move, protects our organs, synthesizes blood cells, and stores nutrients such as calcium.
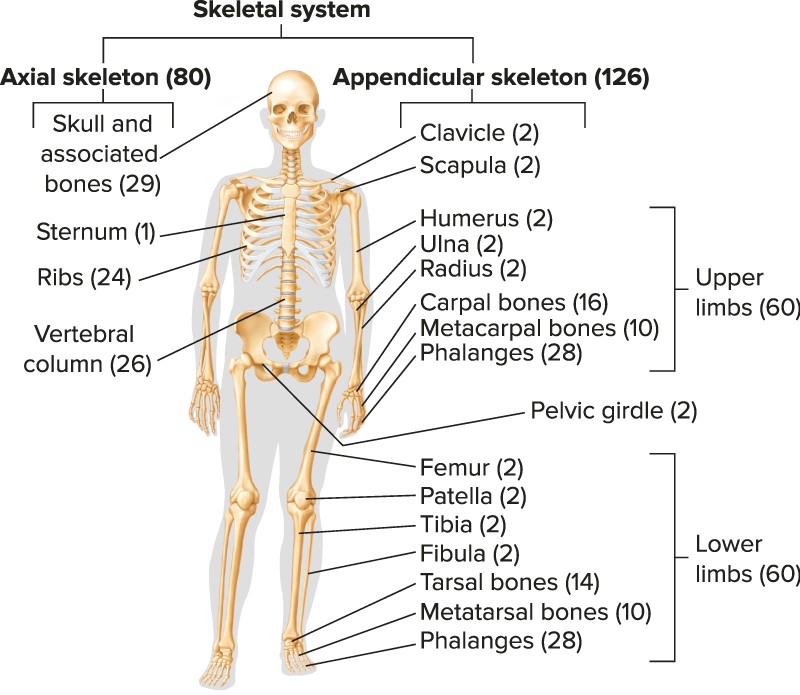
Basic structures and functions
Macroscopic structures
-
Contact bone → stores nutrients, facilitate movement, provide protection
Contact bone stores calcium, which is crucial for our nervous system to function. It also enables us to move and protects our organs. For example, skull protects brain whereas ribs protects heart.
-
Spongy bone → synthesizes red blood cells
Spongy bone contains red marrow that synthesizes red blood cells. Red blood cells bring oxygen throughout our body and release carbon dioxide to our lungs.
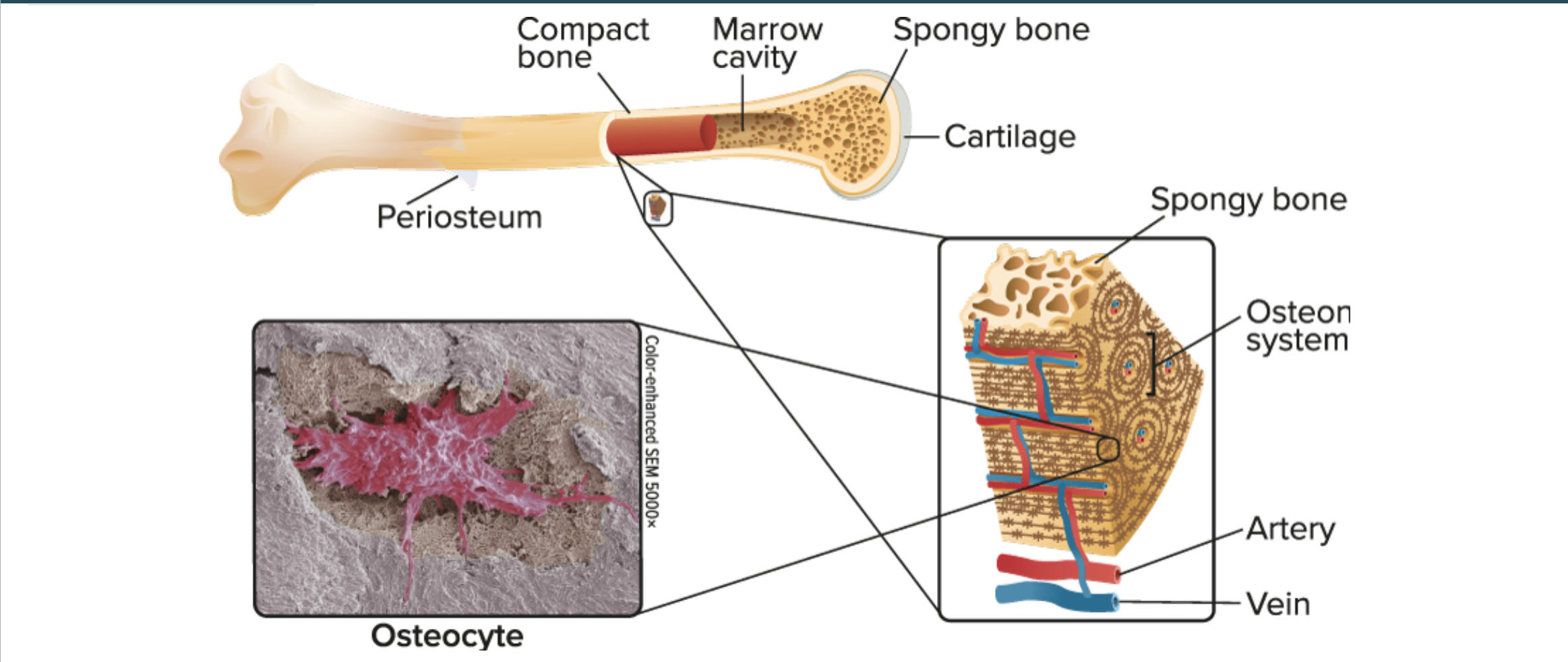
Microscopic structures
-
Marrow cavity → synthesizes blood cells, store fat
Marrow cavity is found within long bones. It contains two types of bone marrow — red and yellow. The red bone marrow mainly synthesizes red blood cells and white blood cells. Yellow bone marrow synthesizes some white blood cells. It is made mostly out of fat and produces fat and bone cells.
-
Periosteum → provide sensation to the bone
Periosteum is a layer of connective tissue that covers the outer surface of bones. It contains a lot of nerves that provide sensation when the tissue is damaged.
Connection to other systems
The skeletal system interacts with the nervous system. The skull protects the brain, which is where all the nerves ultimately meet. Contact bones store calcium, which is essential for nerve cells to transmit signals. The nerves located on the joints or bones provide information of the position of the body for the bones. Periosteum that is located on the outer surface of bones provide sensation when the tissue is injured or damaged.
Differences between a frog and human
Frogs and human have similar skeletons in terms of their limbs. Similar to human, frogs have radius and ulna as their lower arm bones, humerus as their upper arm, femur as their thigh bone, and tibia and fibula as their lower leg bones. However, frogs do not have ribs or pelvis. A frog consists only nine vertebrae that make up their backbone. On the other hand, an adult human usually have 24 vertebrae, since human has a larger spinal cord to protect and support.